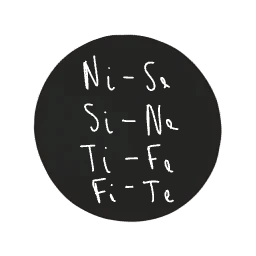
Each cognitive function exists in dynamic tension with its opposite. These function pairs create a self-regulating system, balancing internal and external perspectives, abstraction and concreteness, logic and values, tradition and innovation.
Ni (Introverted Intuition) vs. Se (Extraverted Sensing)
Nature of the Opposition:
- Ni (Inward abstraction, foresight, symbolic meaning) operates by recognizing deep patterns and predicting outcomes.
- Se (Outward sensation, real-time engagement, direct experience) thrives on responding to immediate stimuli.
Why Ni Needs Se:
- Reality Check: Ni’s visionary insights can become detached from reality without Se to ground them in sensory facts.
- Practical Application: Ni sees possibilities, but Se ensures they work in the real world.
- Decisiveness: Ni is slow and contemplative; Se pushes action when needed.
Why Se Needs Ni:
- Depth & Strategy: Se enjoys the moment, but Ni provides long-term vision and meaning.
- Avoiding Impulsivity: Se acts fast; Ni warns of consequences.
- Symbolic Insight: Se perceives, but Ni interprets underlying patterns.
Psychological Tension:
- Ni-dominants (INFJ/INTJ) struggle with engaging in the present.
- Se-dominants (ESFP/ESTP) may lack foresight and strategic depth.
Si (Introverted Sensing) vs. Ne (Extraverted Intuition)
Nature of the Opposition:
- Si (Internalized experience, stability, precedent-based thinking) relies on familiarity and tested knowledge.
- Ne (External possibilities, pattern divergence, exploration) thrives on jumping between ideas and exploring the unknown.
Why Si Needs Ne:
- Adaptability: Si preserves stability, but Ne helps it adjust to new ideas.
- Innovation: Si applies past wisdom; Ne introduces creative alternatives.
- Big Picture Thinking: Si is detail-oriented; Ne connects ideas broadly.
Why Ne Needs Si:
- Grounding in Reality: Ne can get scattered; Si anchors it in real-world experience.
- Verification & Reliability: Ne explores, but Si ensures consistency.
- Sustained Focus: Ne jumps between ideas, while Si maintains focus on what works.
Psychological Tension:
- Si-dominants (ISTJ/ISFJ) may struggle with breaking routines.
- Ne-dominants (ENTP/ENFP) may struggle with finishing projects or being practical.
Ti (Introverted Thinking) vs. Fe (Extraverted Feeling)
Nature of the Opposition:
- Ti (Internal logic, precision, analytical detachment) values correctness over consensus.
- Fe (External harmony, empathy, social values) prioritizes relationships and collective well-being.
Why Ti Needs Fe:
- Social Connection: Ti can become overly detached; Fe ensures emotional attunement.
- Communication: Ti refines ideas, but Fe makes them relatable.
- Ethical Considerations: Ti values logic, but Fe ensures decisions consider human impact.
Why Fe Needs Ti:
- Logical Consistency: Fe follows social values, but Ti ensures they are rational.
- Independent Thinking: Fe is influenced by others; Ti questions whether norms make sense.
- Avoiding Emotional Manipulation: Fe is empathetic, but Ti prevents being swayed by emotions alone.
Psychological Tension:
- Ti-dominants (ISTP/INTP) may struggle with emotional expression.
- Fe-dominants (ENFJ/ESFJ) may struggle with over-prioritizing others’ feelings at the cost of logic.
Fi (Introverted Feeling) vs. Te (Extraverted Thinking)
Nature of the Opposition:
- Fi (Internal values, authenticity, personal meaning) prioritizes subjective truth and ethical integrity.
- Te (External logic, efficiency, measurable outcomes) values objective results.
Why Fi Needs Te:
- Practical Execution: Fi has deep ideals, but Te ensures they are acted upon.
- Objective Structure: Fi is subjective, but Te provides logical organization.
- Productivity: Fi is introspective; Te makes things happen.
Why Te Needs Fi:
- Personal Values: Te can become too pragmatic; Fi ensures alignment with deeper meaning.
- Inner Motivation: Te works toward goals, but Fi ensures they are personally fulfilling.
- Avoiding Ruthlessness: Te is about effectiveness, but Fi humanizes decisions.
Psychological Tension:
- Fi-dominants (INFP/ISFP) may struggle with executing their ideas practically.
- Te-dominants (ENTJ/ESTJ) may struggle with emotional depth.
Conclusion: The Self-Regulating System of Cognitive Function Pairs
Each function is counterbalanced by its opposite to prevent overuse and dysfunction:
- Ni-Se: Depth vs. reality
- Si-Ne: Tradition vs. innovation
- Ti-Fe: Logic vs. harmony
- Fi-Te: Efficiency vs. authenticity
This push-and-pull dynamic explains why inferior functions are difficult to access—they represent an unconscious, yet essential balancing force in the psyche.
***